Enabling Batch Processing in Lambda with SQS
Overview
This section outlines the recommended best practices for implementing batch message processing using AWS Lambda with Amazon SQS. This design pattern is a key component in scalable, cost-effective, and resilient event-driven architectures.
What is Batch Processing?
Batch processing refers to the execution of a group of tasks or messages together within a single unit of work.
In AWS, this means one Lambda function invocation handles multiple SQS messages at once rather than processing them individually.
This approach enhances performance and reduces the number of invocations, which in turn reduces cost and latency.
Architectural Rationale
Batch processing is a recommended practice in serverless environments for the following reasons:
Operational Efficiency
Minimizes Lambda invocations by consolidating multiple messages into a single execution cycle.Throughput Optimization
Reduces idle time and cold start frequency, enabling faster overall processing and lower latency under burst loads.Cost Optimization
Reduces the number of billable Lambda invocations, directly impacting overall execution costs.Scalability and Resilience
Handles high-frequency workloads gracefully. In conjunction with features like partial batch response and DLQs, batch processing enhances fault isolation and retry reliability.Design Flexibility
Provides better control over message ordering, timeouts, and concurrency management using FIFO queues and batch windowing.
Implementation Guide
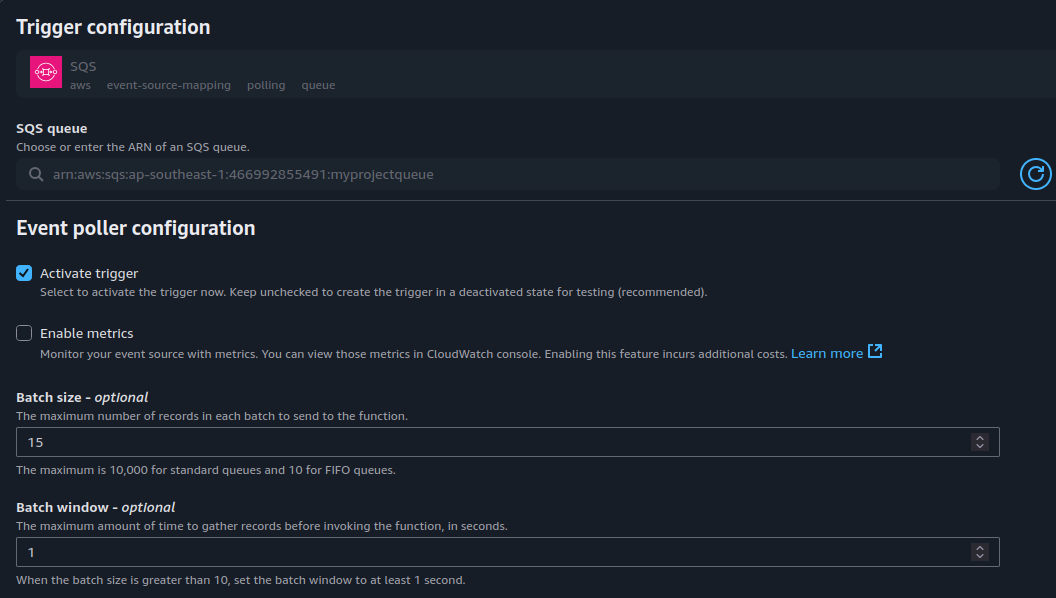
1. Configure Lambda Trigger from SQS
Navigate to AWS Lambda > your target function.
Under the Triggers section, locate and edit the SQS trigger.
Modify the following parameters:
- Batch size
- Up to
10for FIFO queues - Up to
10,000for Standard queues
- Up to
- Batch window (optional)
- Duration (0–300 seconds): Lambda waits to buffer more messages before invoking.
- Batch size
2. Update Lambda Handler to Process Batches
The Lambda function must loop over event.Records to process each message individually within the batch:
export const handler = async (event) => {
console.log(` Received batch of ${event.Records.length} messages`);
for (const record of event.Records) {
const body = JSON.parse(record.body);
console.log(" Processing message:", body);
// Business logic here
}
return { statusCode: 200 };
};
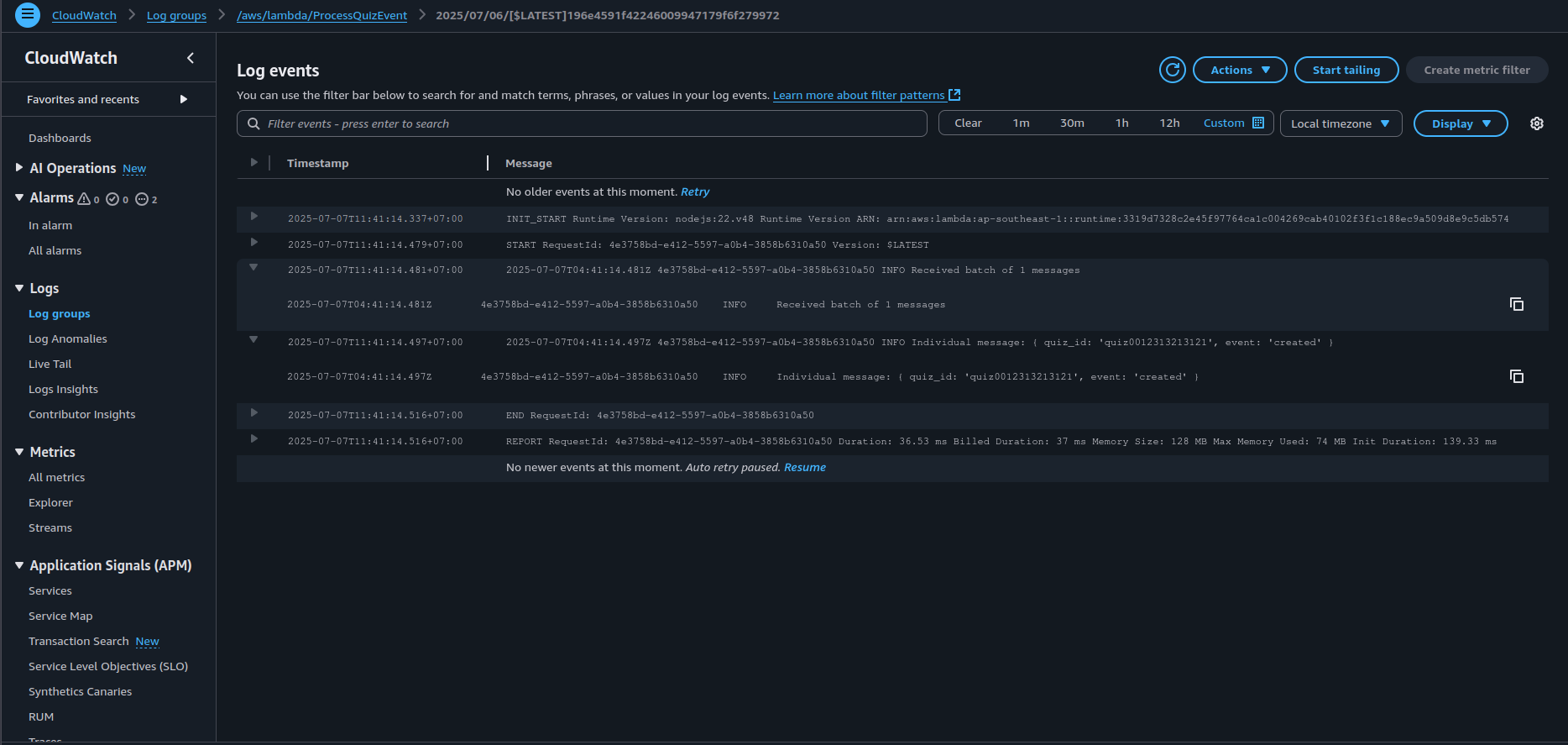
3. Test the Batch Setup
- Send multiple messages to the SQS queue in quick succession.
- Confirm batch aggregation by reviewing CloudWatch Logs.
Expected Output:
Failure Simulation and DLQ Integration
To test failure handling:
- Force an error in one message’s processing loop.
- Observe that the entire batch is retried by default.
Note: Enable Partial Batch Response to allow successful messages to complete while failing messages are retried.
Configure a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) for the SQS queue to capture failed messages after maxReceiveCount is reached.
Monitoring and Observability
Use the following CloudWatch Metrics for insight and alerting:
ApproximateNumberOfMessagesNotVisible→ Messages currently being processedNumberOfMessagesDeleted→ Successfully processed and removed from the queueNumberOfMessagesReceived→ Incoming workloadIteratorAge→ Delay between message enqueue and processing
Enable structured logging and consider using AWS X-Ray for tracing.
Summary
Batch processing in Lambda provides a scalable and cost-efficient way to process high-throughput SQS workloads. With proper tuning and observability, it becomes a foundational pattern in resilient, event-driven cloud architectures.